Key Takeaway
Edge computing enhances various sectors by enabling real-time insights and operational efficiency. In manufacturing, AI models detect irregularities and forecast maintenance. Healthcare facilities utilize edge technology for real-time patient monitoring, while financial institutions benefit from faster fraud detection and personalized services, all while adhering to regulatory standards. Security is crucial; local data processing minimizes exposure, and zero-trust architectures ensure data protection. Future advancements will focus on seamless orchestration between edge and cloud environments, allowing organizations to optimize workloads based on security and regulatory needs, ultimately enhancing agility and insights without compromising centralized systems.
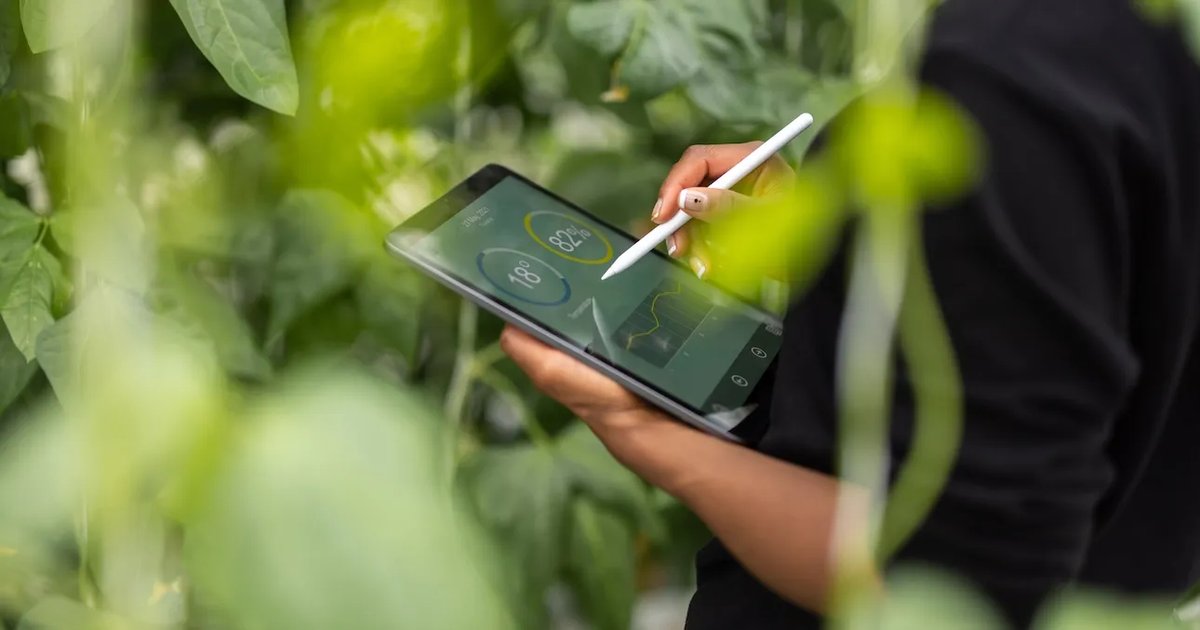
Consider manufacturing and production. AI models implemented on-site assist plants in identifying irregularities and predicting maintenance needs, resulting in smoother operational continuity.
Healthcare facilities utilize edge technology to provide real-time patient monitoring through methods that are independent of network bandwidth.
Financial institutions are adopting edge computing to enhance fraud detection speed, facilitate real-time transaction approvals, and offer hyper-personalized customer experiences, all while adhering to strict regulatory and data residency standards.
Edge computing enhances the accessibility and scalability of AI by enabling real-time insights directly at the data source.
How crucial are cybersecurity and compliance in modern edge computing?
While speed and insight are vital, they are insufficient without robust security and governance at the edge.
Workload distribution can occur without sacrificing security measures.
Edge computing safeguards sensitive data through local processing, which reduces exposure during data transfers.
Zero-trust architectures, along with data encryption and secure boot procedures, have become standard practices that bolster the security of edge deployments by restricting access to authorized users, protecting data both at rest and in transit, and ensuring that only verified software operates on edge devices—thereby minimizing the attack surface across distributed environments.
Additionally, edge models help entities adhere to local regulations and data sovereignty laws, especially in areas with strict guidelines regarding personal data usage.
Security and compliance are essential for successful edge deployment—they are not optional add-ons.
What does the future hold for edge computing?
Looking forward, the real opportunity lies in seamless orchestration between edge and cloud environments.
Systems that enable the intelligent movement of workloads based on security, latency, or regulatory needs will yield the highest ROI.
Forward-thinking organizations will view edge computing as a significant advancement that complements—rather than replaces—centralized systems, allowing enterprises to respond swiftly, mitigate risks, and generate insights exactly where and when they are needed.












96 Comments